Some pharmacokinetic data and dosage regimen of danofloxacin after intravenous administration in Nili-Ravi and Kundhi buffaloes
Keywords:
Buffaloes, Bubalus bubalis, Pharmacokinetics, Danofloxacin, Dosage regimen, Plasma protein binding, Kundhi buffaloes, Intravenous administration, PakistanAbstract
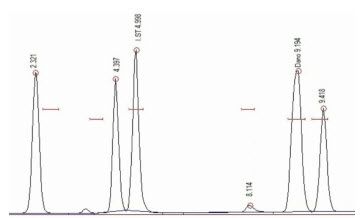
Danofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic which is extensively used against a variety of bacterial infection in animals worldwide except in Pakistan. The optimal dosage regimen of danofloxacin was necessary in order to use this drug therapeutically and to minimize the emergence of bacterial resistance in local buffaloe breeds in Pakistan. For this, the present study aimed to investigate the pharmacokinetics behavior and optimal dosage regimen of danofloxacin in 16 adult healthy buffaloes, 8 each of Nili-Ravi and Kundhi breed following single intravenous administration at the dose of 2.5 mg/kg body weight. Blood samples (5 ml) were drawn from jugular vein in heparinized plastic centrifuge tubes at zero and 0.083, 0.167, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24 h after injection and drug concentrations in plasma were measured by HPLC method. The distribution of drug was rapid whereas elimination was low in both breeds. Volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) was significantly (P LT 0.05) higher in Kundhi buffaloes indicating the extensive distribution of danofloxacin in Kundhi than NiliRavi buffaloes. However, the total body area covered by drug was remarkably lower in Kundhi than Nili-Ravi buffaloes as indicated by lower values of area under concentration time curve (AUC) in Kundhi than Nili-Ravi buffaloes. Total body clearance (ClB) was significantly (P LT 0.05) faster in Kundhi buffaloes than Nili-Ravi buffaloes. The mean residence time (MRT) was noted to be (Mean±SD) 4.78±0.52 and 4.44±0.37 h in NiliRavi and Kundhi buffaloes respectively. On the basis of pharmacokinetic parameters, suitable intravenous dosage regimens for danofloxacin in Nili-Ravi and Kundhi buffaloes would be 6.5 and 8.3 mg/kg to be repeated after 12 h intervals. The present study is the foremost pharmacokinetics study of danofloxacin in the local species which would provide the valuable contribution in the local manufacturing of danofloxacin in Pakistan in future.
Downloads
Metrics




.png)








