A novel SNP (c.258+43C>T) in LPL gene and association with milk production in buffaloes
Keywords:
Bubalus bubalis, Polymorphism, buffaloes, Genetic Diversity, LPL gene, Azakheli, Nili-Ravi, polymorphism, genetic diversityAbstract
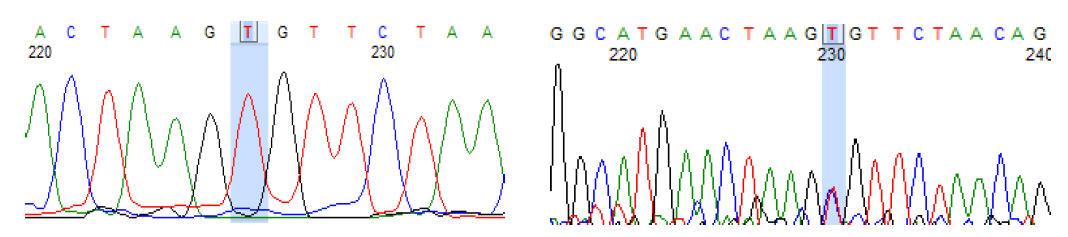
Buffalo milk is the most preferred commodity in Pakistan due to high fat contents. Hydrolysis of circulating triglycerides and uptake of fatty acids in the mammary gland is regulated by lipoprotein lipase (LPL). T his study is designed to identify single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in LPL gene among high and low milk producing buffalo breeds of Pakistan. We selected samples (n=50) of each Nili-Ravi a high milk producing and Azakheli a low milk producing buffalo breeds. Blood samples were collected for DNA extraction. LPL region of exon 2 region along with exon/intron boundaries were sequenced and data was analyzed for variation detection. Allele frequency was calculated using Hardy-Weinberg equation and in-silico analysis was performed for functional prediction and genetic diversity assessment. We found one single nucleotide polymorphism c.258+43C>T in the intronic region of LPL gene. This polymorphism followed the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in both Nili-Ravi (P-value = 0.538) and Azakheli (P-value = 0.077). Association of T-allele analysis predicted it significantly higher (P-value = 0.009) in Nili-Ravi. We found one novel SNP (c.258+43C>T) in the LPL gene in both high and low milk producing buffalo breeds of Pakistan but high in Nili-Ravi. Lower splice site effect suggests its less strength of association with milk producing trait.
Downloads
Metrics




.png)








