Prevalence and sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus causing mastitis in buffaloes around Lahore, Pakistan
Keywords:
Bubalus bubalis, buffaloes, mastitis, Staphylococcus aureus, california mastitis test, antibioticsAbstract
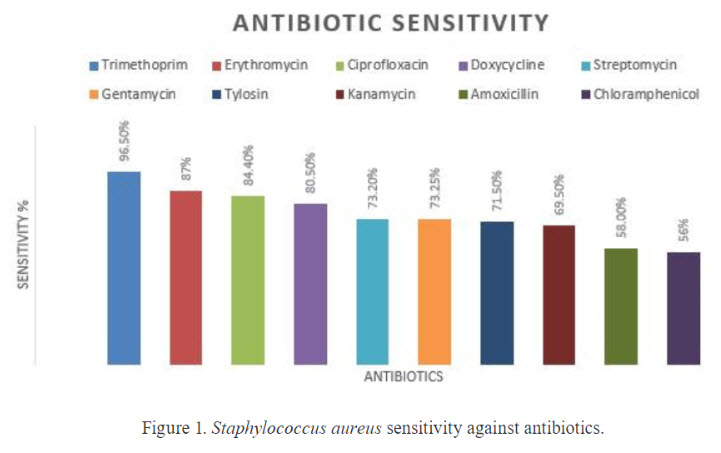
The present study determined the prevalence and antibiotic sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus causing mastitis in buffaloes around Lahore, Pakistan. Clinical mastitis was diagnosed on the basis of physical examination of the udder, teat and the physical appearance of the milk. Subclinical mastitis was diagnosed on the basis of the California Mastitis Test. Among a total of 598 buffaloes, 332 were found to have mastitis (55.5%). A total of 449 mastitic milk samples from different animal quarters were collected from different livestock farms from peri-urban area of Lahore of which 16% (71/449) and 84% (378/449) were clinical and subclinical, respectively. The animal prevalence of mastitis was 55.5% with 95% Confidence interval of 51.5 to 59.4, while prevalence per quarter was 18.7% with 95% Confidence interval of 17.4 to 20.3. From these 449 milk samples, 257 isolates of Staphylococci were obtained. A Staphytect plus test confirmed 65% (95% CI 58.9 to 70.6) isolates as coagulase positive Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotic sensitivity of all coagulase positive Staphylococcus aureus was performed by disk diffusion method. The zone of inhibition of antibiotics trimethoprim, erythromycin, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, streptomycin, gentamycin, tylosin, kanamycin, amoxicillin and chloramphenicol were measured as 96.5%, 87%, 84.5%, 80.5%, 73.3%, 73.2% 71.5%, 69.5%, 58% and 56.5%, respectively.
Downloads
Metrics




.png)








