Characterization of Pasteurella multocida isolates of buffalo origin from Gujarat state of India by outer membrane protein profile analysis
Keywords:
Buffaloes, Bubalus bubalis, Pasteurella multocida, Outer membrane protein, SDS-PAGE, Major protein, Iron regulated outer membrane protein, Diseases, Effect of the disease, Vaccine, Gujarat state, IndiaAbstract
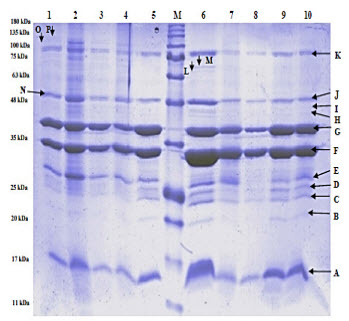
Haemorrhagic septicaemia caused by Pasteurella multocida is one of the most fatal diseases affecting Indian buffaloes. The disease is of high economic significance in India due to the high mortality rate in the affected population. The outer membrane proteins (OMPs) are virulence factors of P. multocida which play an important role in the pathogenesis of Pasteurellosis. In the present study, P. multocida B: 2 field isolates (n=7) and a vaccine strain (P52) were grown under normal and iron restricted conditions. OMPs were extracted by sarkosyl method. Characterization of OMP rich extracts from isolates grown under normal conditions by sodium dodecyl sulphatepolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) revealed a total of 11 to 13 bands of about 16 to 86 kDa. Two bands of molecular weights 68 and 71 kDa were present only in the OMP profile of vaccine strain. Under iron restricted conditions, two additional protein bands of molecular weights 112 and 125 kDa were expressed in all isolates including the vaccine strain. Based on band intensity, 31 and 37 kDa proteins were assumed to be the major proteins expressed under both normal and iron restricted conditions. Further studies are required to study the role of major proteins and iron regulated outer membrane proteins (IROMPs) in the virulence of the bacteria.
Downloads
Metrics




.png)








