Multilocus sequence typing of P. multocida isolates of buffalo origin from Gujarat state of India
Keywords:
Buffaloes, Bubalus bubalis, Pasteurella multocida, Multilocus sequence typing, Gujarat, Sequence type, Allelic profileAbstract
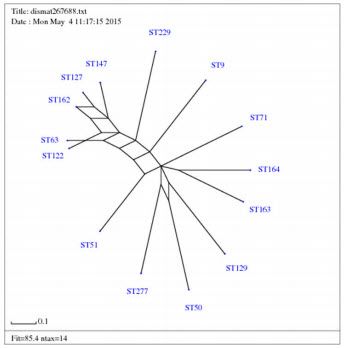
Haemorrhagic septicaemia in Indian buffaloes is mainly caused by Pasteurella multocida serotype B: 2. The present study was conducted to characterize the P. multocida serotype B: 2 isolates of buffalo origin by multilocus sequence typing (MLST) to identify the sequence types prevailing around Gujarat state in India. A total of seven field isolates collected from different regions across the state and a reference strain (P52) were used for this study. Seven housekeeping genes were specifically amplified by PCR; the gene sequences obtained were trimmed to specific length and allelic profiles were assigned to these seven loci. The assigned allelic profiles were 23, 37, 21, 17, 4, 2 and 17 for adk, est, pmi, zwf, mdh, gdh and pgi genes, respectively and all the isolates were grouped in one sequence type, sequence type 122 (ST122). eBURST analysis classified ST122 into group number 23 when group definition was 5 or more matches. But when group definition was 6 or more matches it was classified into group number 22 along with ST63. Phylogenetic and Splits Tree analysis showed that ST122 is closely related to ST63, ST127, ST162 and ST147 and all five of them were grouped in a cluster. From the study it was concluded that ST122 may be the predominant sequence type in buffaloes of Gujarat state.
Downloads
Metrics




.png)








