The influencing of canopy gap and conspecific adult tree determined the characteristic of dominant species in Ban Se Pa La freshwater swamp forest, Umphang District, Tak Province
Keywords:
species composition, fresh water swamp forest, forest dynamics, Tak ProvinceAbstract
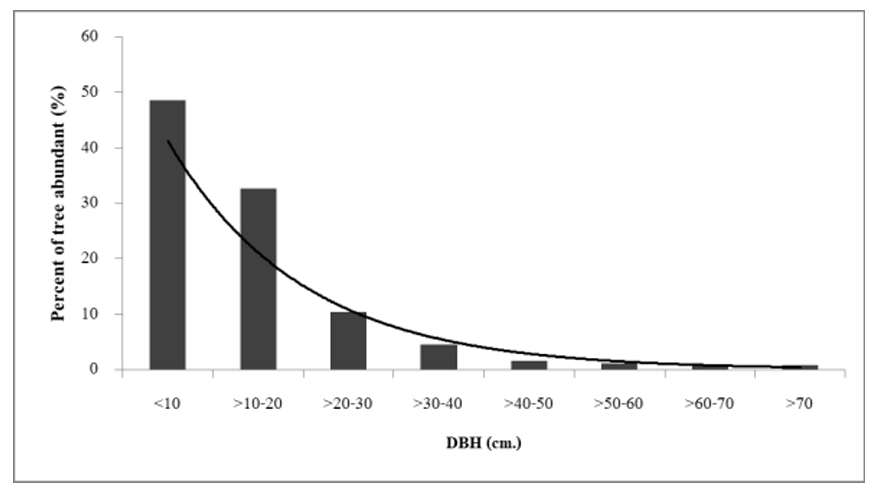
The study goal investigated species composition and the dominant species characteristics which the affected by canopy gap and conspecific adult tree in Ban Se Pa La freshwater swamp forest, Umphang district Tak province. Methodology was three belt plots of 10 m. x 300 m. and established for measuring the species composition. Tree species with a diameter at breast height ? 1 cm. so, measure and identify, analyze the correlation with canopy gap and conspecific adult tree of them. The results explained a total of 64 species 45 genera and 30 families from 2,512 stems. This community showed diversity index 2.75, basal area and stems densities 40.56 m2/ha, and 1,428 stem/ha, respectively. A top ten of dominant species base on the important value index were Elaeocarpus grandiflorus, Syzygium hulletianum, Pometia pinnata, Pandanus tectorius, S. siamense, S. cumini, Calophyllum sp., Salix tetrasperma, Erythrina subumbrans, Nauclea subdita. Moreover, the sapling of dominant species determined by canopy gap and conspecific adult tree, divided into 3 characteristic group including: 1) shade tolerance species were E. grandiflorus, P. pinnata, S. siamense, and C. sp., 2) light demanding species were S. tetrasperma and N. subdita, and 3) generalist species were S. megacarpum, S. cumini, S. thorelii and S. hulletianum. This result has been suggesting the considering of these dominant species characteristics for restoring the degraded freshwater swamp forest that assist in rapid successfully.
Downloads


.png)





