Structure and Carbon Sequestration of Natural and Economics Forest at Wang Nam Khiao Forestry Research and Student Training Station, Nakhon Ratchasima Province
Keywords:
Carbon Sequestration, Economics Forest, Natural Forest, Wang Nam Khiao Forestry Research and StudentAbstract
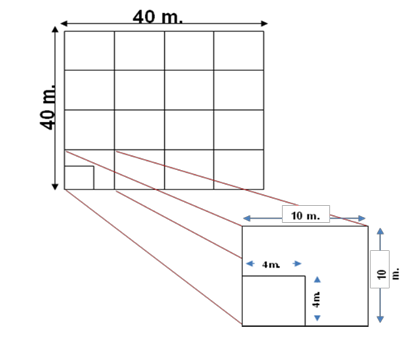
The purpose of this study was to examine vegetation structure and carbon sequestration of Natural and Economics Forest at Wang Nam Khiao forestry research and student training station, Nakhon Ratchasima Province in 8 plots , 40 x 40 m2 in size. Results show that total of species in Dry Evergreen forest were 95 species (76 genera, 45 families) and the most dominant trees were Hydnocarpus ilicifolia King, Wrightia arborea (Dennst.) Mabb.) and Afzelia xylocarpa (Kurz) Craib). The total of species in Eucalyptus Plantation were 20 species (19 genera, 13 families) and the most dominant trees were Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh., Leucaena leucocephala (Lam.) de Wit and Grewia eriocarpa Juss. The Shanon-Wiener index of diversity in Dry Evergreen forest and Eucalyptus Plantation were 3.726 and 0.465, respectively. Carbon sequestration in Dry Evergreen forest and Eucalyptus Plantation were 94.57 tC/ha equivalent to 347.07 tCO2e/ha and 45.81 tC/ha, equivalent to 168.11 tCO2e/ha
Downloads


.png)





