IMPACT OF ESTRADIOL BASED MODIFIED SYNCHRONIZATION PROTOCOL ON EXHIBITION OF BEHAVIOURAL ESTRUS IN BUFFALO (Bubalus bubalis)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56825/bufbu.2025.4434322Keywords:
Bubalus bubalis , buffaloes, behavioral estrus, heat synch, G6G-Heatsynch, artificial insemination, uterine toneAbstract
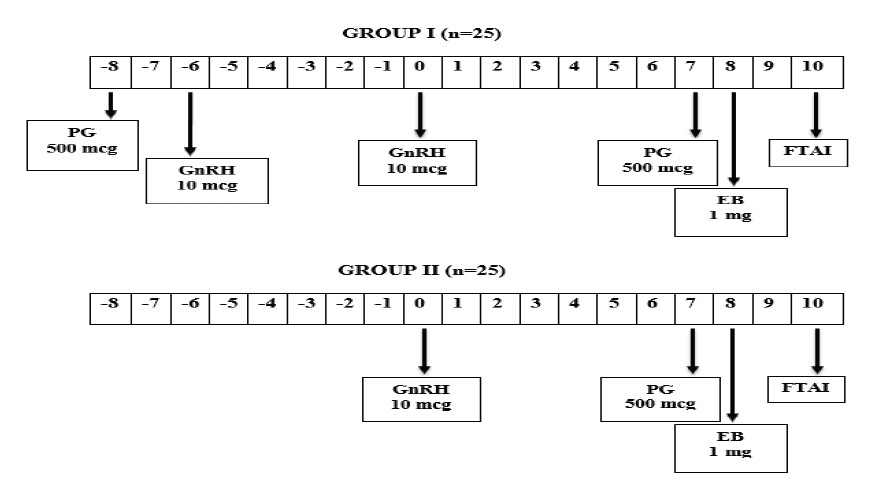
The present study was aimed to compare the behavioral estrus signs and uterine tone exhibited by buffaloes subjected to traditional heat synch and a modified heat synch (G6G-Heatsynch) protocol in which a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) injection was administered two days after prostaglandin (PGF2α) and six days prior to the Heat synch protocol. A total of 50 postpartum clinically healthy and cyclic buffaloes were randomly divided into two groups. Buffaloes of Group 1 (n=25) were treated with G6G-Heatsynch protocol whereas Group 2 (n=25) buffaloes received the traditional Heat synch protocol. Various behavioral estrus signs viz. frequent urination, vulvar swelling, cervical-vaginal mucus (CVM) discharge, bellowing and uterine tonicity were recorded on the day of fixed time artificial insemination (FTAI) and a comparison was carried out between both groups based on display of these estrus signs. Frequent urination, vulvar swelling and bellowing were present in all the animals of both groups whereas CVM was observed in 80 and 68% buffaloes of Group 1 and 2, respectively. High uterine tone was exhibited by 44% buffaloes of Group 1 compared to 32% buffaloes of Group 2. Furthermore, frequent urination, vulvar swelling and bellowing were observed in all the animals of both groups irrespective of their subsequent pregnancy status. On the other hand, higher proportion of pregnant buffaloes showed CVM discharge compared to non-pregnant ones in Group 1 (P<0.01) and 2 (P<0.05). Pregnant buffaloes also had higher uterine tonicity at the time of FTAI than non-pregnant buffaloes of Group 1 (P<0.05) and 2 (P<0.01). In conclusion, estradiol-based synchronization methods were successful in eliminating estrus detection problem. Further, CVM discharge and high uterine tonicity at the time of AI were prominent signs to predict successful pregnancy in buffaloes subjected to estradiol-based synchronization protocols.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Alapati, A., S.R. Kapa, S. Jeepalyam, S.M.P. Rangappa and K.R. Yemireddy. 2010. Development of the body condition score system in Murrah buffaloes: validation through ultrasonic assessment of body fat reserves. J. Vet. Sci., 11(1): 1-8. DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2010.11.1.1
Anitha, A., K.S. Rao, J. Suresh, P.S. Moorthy and Y.K. Reddy. 2011. A body condition score (BCS) system in Murrah buffaloes. Buffalo Bull., 30(1): 79-99. Available on: https://kukrdb.lib.ku.ac.th/journal/BuffaloBulletin/search_detail/result/286325
Baruselli, P.S., H.E. Maduriera, V.H. Barnabe, R.C. Barnabe and R.C. de Araujo Berber. 2003. Evaluation of synchronization of ovulation for fixed timed insemination in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Research and Animal Science, 40(6): 431-442. DOI: 10.1590/S1413-95962003000600007
Bilal, A.G., S.S. Dhindsa, D. Dadarwal, M. Honparkhe, S.P.S. Ghuman and P.S. Brar. 2017. Influence of behavioural estrus signs on pregnancy rates in buffaloes subjected to modified synchronization protocols. Indian Vet. J., 94: 81-83.
De Rensis, F. and F. Lopez-Gatius. 2017. Protocols for synchronizing estrus and ovulation in buffalo (Bubalus bubalis): A review. Theriogenology, 67(2): 209-216. DOI: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2006.09.039
Dhindsa, S.S., M. Honparkhe, D. Dadarwal, P.S. Brar and R.S. Grewal. 2016. Fertility enhancement through doublesynch protocol in buffalo during summer season. Indian Vet. J., 93(10): 17-19.
Kumaresan, A., M.R. Ansari and P.C. Sanwal. 2001. Assessment of accuracy of oestrus detection by progesterone assay in cattle and buffaloes. Indian J. Anim. Sci., 71(8): 34-36.
Mirmahmoudi, R. and B.S. Prakash. 2014. Temporal changes in endogenous estrogens and expression of behaviors associated with estrus during the periovulatory period in doublesynch treated Murrah buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis). Iranian Journal of Applied Animal Science, 4(3): 499-504.
Mohan, K., Nitu and B.S. Prakash. 2014. Evaluation of the Heatsynch protocol in Murrah buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) during hot summer season. J. Anim. Res., 4(2): 241-246. DOI: 10.5958/2277-940X.2014.00010.2
Moreira, F.C., C.A. Orlandi, C.A. Risco, R. Mattos, F. Lopes and W.W. Thatcher. 2001. Effects of presynchronization and bovine somatotropinon pregnancy rates to a timed artificial insemination protocolin lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci., 84(7): 1646-1659. DOI: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(01)74600-0
Navanukraw, C., D.A. Redmer, L. Reynolds, J.D. Kirsch, A.T. Grazul-Bilska and P.M. Fricke. 2004. A modified presynchronization protocol improves fertility to timed artificial insemination in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci., 87(5): 1551-1557. DOI: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73307-X
Pancarci, S.M., E.R. Jordan, C.A. Risco, M.J. Schouten, F.L. Lopes, F. Moreira and W.W. Thatcher. 2002. Use of estradiol cypionate in a presynchronized timed artificial insemination program for lactating dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci., 85(1): 122-131. DOI: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(02)74060-5
Sandhu, H.S., S.S. Dhindsa, M. Honparkhe, B. Singh, S. Singhal and R. Jindal. 2017. Relationship between estrus signs and subsequent fertility rates in buffaloes subjected to estradiol based synchronization treatments. Theriogenology Insight., 7(3): 199-203. DOI: 10.5958/2277-3371.2017.00038.9
Singh, H. 2017. Ovarian and fertility responses following estradiol based modified synchronization protocol in buffaloes. M.V.Sc. Thesis, Guru Angad Dev Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
Vale, W.G., O.M. Ohashi, J.S. Sousay and H.F.L. Ribeiro. 1990. Studies on the reproduction of water buffalo in the Amazon basin. p. Livestock Reproduction in Latin America, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria.
Verma, K.K., S. Prasad, T.K. Mohanty, A. Kumaresan, S.S. Layek, T.K. Patbandha and S.C. Kantwa. 2014. Behavioural signs of estrus in different parity of Murrah buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis): A comparative study. Indian J. Anim. Res., 48(6): 620-624. DOI: 10.5958/0976-0555.2014.00043.0
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Buffalo Bulletin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








.png)








