TLR-4 gene polymorphism in Indian Murrah buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis)
Keywords:
Bubalus bubalis, buffaloes, TLR4 gene, Murrah buffaloes, PCR-RFLP, Bsp1286IAbstract
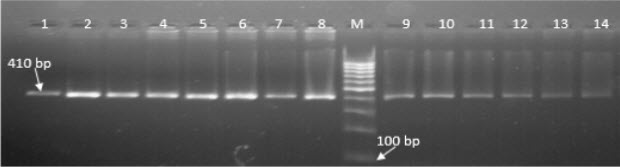
TLR-4 is an important candidate gene, which affects the host disease resistance. Its role in pathogen recognition and subsequent initiation of the inflammatory and immune responses makes it a suitable candidate gene for enhancing disease resistance in dairy animals. TLR-4 gene also provides an ideal model to study the consequences of genetic variation and their relation to the function of receptor and their susceptibility to diseases. TLR-4 gene mainly recognizes the conserved lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid patterns of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, respectively. The present study was undertaken with the objectives of sequence characterization and studying the genetic variation in exon 3 of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) gene in Murrah buffalo by PCR-RFLP. Exon 3 (2265 bp) of TLR-4 gene was amplified by PCR using oligonucleotide primers designed by Primer 3 plus software and subsequently, RFLP study was carried out to identify genotypes of the animals with Bsp1286I restriction enzyme. It exhibited AA, AB and BB genotypes in exon 3 for primer 3.1, 3.5, 3.6 and 3.7. Amplicons were sequenced and compared with published Bubalus bubalis (EU386358) sequence and variation at four nucleotide positions were occurs and out of which one non synonymous SNP result into change of amino acid (Threonine to Glutamine).
Downloads
Metrics




.png)








