Effect of per-vaginal insertion of once-used TRIU-B on post-ovulation plasma progesterone and conception rate in buffalo
Keywords:
Bubalus bubalis, buffaloes, conception, progesterone, TRIU-BAbstract
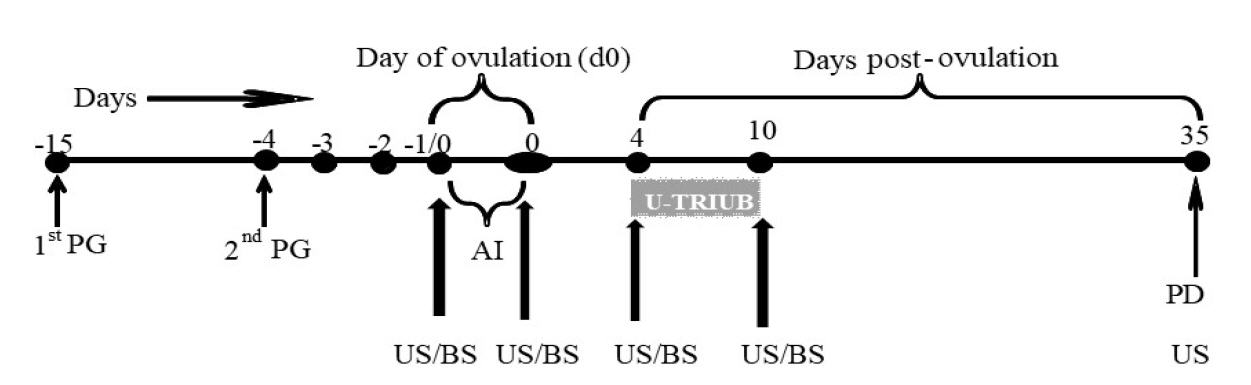
The present study evaluated the impact of once-used intravaginal progesterone inserts (TRIU-B) from day 4 to day 10 post-ovulation on luteal profile (corpus luteum diameter, CL; plasma progesterone) and conception rate in buffalo (n=80) during summer season. The buffaloes were estrus synchronized by Cloprostenol (500 μg, i.m.) administered 11 days apart, followed by AI during standing estrus. All the buffaloes were equally categorized into control (without TRIU-B) or treatment (pervaginally inserted with once-used TRIU-B) group. From each group, 15 buffaloes were subjected to ovarian ultrasonography for CL diameter measurements on day 4 and day 10 postovulation followed by jugular vein blood collection for plasma progesterone analysis. On day 10 postovulation, the control group buffalo had larger (P<0.05) CL diameter (15.2±0.5 vs. 14.0±0.3 mm), whereas, plasma progesterone was higher (P<0.05) in treatment group (3.4±0.2 vs. 1.7±0.1 ng/ml). Conception rates were 55.0 and 37.5% in treatment and control groups, respectively (χ2=2.46, P>0.05). Moreover, pregnant and non-pregnant buffalo of treatment group exhibited higher (P<0.05) plasma progesterone on day 10 post-ovulation compared to their control counterparts. In conclusion, pervaginal insertion of once-used TRIU-B enhanced post-ovulation plasma progesterone but failed to improve conception rate in buffalo.
Downloads
Metrics




.png)








