Investigations of foot and mouth disease outbreaks in different districts of Punjab, Pakistan
Keywords:
Bubalus bubalis, Foot and mouth disease, buffaloes, Outbreaks, foot and mouth disease, Serotypes, ruminants, serotypes, IS ELISA, PunjabAbstract
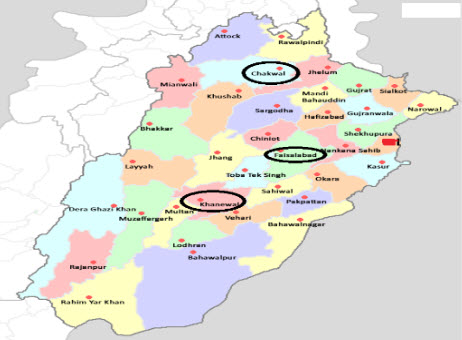
Foot and mouth disease (FMD) is an endemic and highly contagious disease of ruminants and its outbreaks had always remained a threatening problem in Pakistan. The aim of the present study was to determine the prevalence of FMD and its serotypes in ruminants of different districts of Punjab. Sampling was performed from outbreaks of foot and mouth disease in different districts of Punjab, Pakistan including Khanewal, Faisalabad and Chakwal. An indirect sandwich Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) was employed for the detection and typing of Foot and mouth disease virus. A total of 19 outbreaks in cattle, buffaloes, sheep and goats suspected of FMD were attended, investigated and 109 epithelial tissue samples (42 from buffaloes, 54 from cattle, 10 from goats and 3 from sheep) were collected. A total of 77 (70.65%) samples were found positive for FMD virus. Out of these positive samples, 48 were successfully typed into serotype O (62.33%) followed by 26 (33.77%) into Asia I and 3 (3.90%) into serotype A. FMD was more prominent in Faisalabad as compared to Khanewal and Chakwal. The disease and all its three serotypes were predominant in cattle (85.18%) as compared to buffaloes (64.28%) and goats (40%). The results of the present study showed that FMD is very common disease in large as well as small ruminants of Pakistan and a proper vaccination program should be planned and implemented for its control to avoid the losses caused by this devastating disease.
Downloads
Metrics




.png)








