การคำนวณและจำลองโหมดแสงพลาสมอนิก TM0 เพื่อประยุกต์ท่อนำแสง เป็นอุปกรณ์ตรวจวัด | Computation and Simulation of TM0 Surface Plasmonic Mode for Sensor Waveguide Application
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.main##
บทคัดย่อ
The TM0 mode power transfer in surface plasmonic slot waveguide computed and simulated in this research for sensor waveguide applications while the gap slot refractive index of two Au thin films was changed from 1.34 to 1.49 in gap slot width of 100 nm, 200 nm 400 nm of waveguide and 1000 nm, 1050 nm, 1150 nm 1300 nm and 1500 nm input wavelength. The result of computation showed that the TM0 mode power transfer changed when refractive index and input wavelength changed, this showed some significance of ability in sensor application. The 4 mm long and 70 nm gap width of slot waveguide was set as single and two and four slots line simulation model, FDTD method in optiwave software was used for this simulation, refractive index of gap slot changed in simulation. The result of simulation showed that TM0 mode was depended on gap refractive index also, slope and lose peak of TM0 mode intensity in graph of simulation result of single slot two slot and 4 slot waveguide showed most significance as sensor application was in 4 slots line. Also in refractive index of cladding change, some external solution layers were added on the top of two Au metal slot thin films of single slot waveguide, this model was simulated in many times with 1 and 1.33 and 1.4 refractive index of the solution layers and input wavelength varied from 1000 nm to 1350 nm, TM0 mode intensity data corrections in each time were plotted in graphs. The result showed that there were more lose peak wavelength ship in each refractive index of thin solution layers. This showed good significance in sensor applications.
บทคัดย่อ
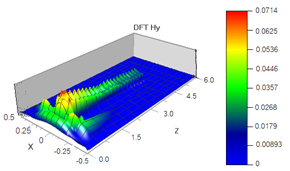
ในงานวิจัยนี้ได้ออกแบบโปรแกรมแมทแล็บ เพื่อคำนวณกำลังแสงส่งผ่านในท่อนำแสงเชิงผิวแบบซองว่างแผ่นฟิล์มโลหะคู่ โดยการเปลี่ยนค่าดัชนีหักเหแสงยังผลของซองว่างแผ่นฟิล์มทอง เพื่อตรวจสอบรูปแบบที่เป็นไปได้ในการประยุกต์เป็นอุปกรณ์ตรวจวัด คำนวณโดยเปลี่ยนค่าดัชนีหักเหแสงตั้งแต่ 1.34 ถึง 1.49 และเปลี่ยนความกว้างซองว่างระหว่าง 100 nm ถึง 400 nm และใช้ความยาวคลื่นระหว่าง 850 ถึง 1500 nm พบว่ากำลังแสงส่งผ่านตามความยาวของซองว่างที่ตั้งฉากกับแผ่นฟิล์มทองที่เรียกว่า โหมดแสงเชิงผิวTM0 เกิดการเปลี่ยนแปลงไปเมื่อดัชนีหักเหแสงและความยาวคลื่นเปลี่ยนแปลงค่าไป และแสดงความสัมพันธ์เป็นแบบเชิงเส้น ซึ่งอาจประยุกต์ทำเป็นอุปกรณ์ตรวจวัดได้ และได้ออกแบบท่อนำแสงความยาว 4mm ความกว้างซองว่างแผ่นฟิล์มทอง 70 nm แบบซองว่างแผ่นฟิล์มทองเดี่ยว แบบสองซองว่างแผ่นฟิล์มทอง และสี่ซองว่างแผ่นฟิล์มทอง เรียงต่อกัน เพื่อจำลองผลเชิงเลขโดยใช้ระเบียบวิธี FDTD ในโปรแกรมออปติเวฟ ซึ่งเปลี่ยนค่าดัชนีหักเหแสงของซองว่างแผ่นฟิล์มทองจาก 1.33 ถึง 1.49 ความยาวคลื่น 950 nm 1050 nm 1150 nm และ 1300 nm และเก็บผลการจำลองสะสมได้กราฟความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างความเข้มแสง TM0 กับความยาวคลื่นที่แปรเปลี่ยนไปตามค่าดัชนีหักเหแสงและความยาวคลื่น ที่มีความชันเส้นกราฟและมีจุดโค้งต่ำสุดกราฟเป็นแบบพีคของแต่ละค่าดัชนีหักเหแสง และแต่ละพีคเลื่อนเหลื่อมกันตามแกนความยาวคลื่นแสงที่ป้อนเข้าไป โดยที่การเลื่อนเหลื่อมเกิดขึ้นชัดเจนสุดที่ท่อนำแสงแบบสี่ซองว่างแผ่นฟิล์มทองเรียงต่อกัน และเมื่อจำลองผลเชิงตัวเลขโดยการเพิ่มชั้นสารละลายบางบนแผ่นฟิล์มบางของทองทั้งสองของท่อนำแสงแบบซองว่างแผ่นฟิล์มทองเดี่ยว และรันโปรแกรมหลายครั้ง ซึ่งใช้ดัชนีหักเหแสงเท่ากับ 1 , 1.3 และ 1.4 แต่ละค่าเปลี่ยนความยาวคลื่นตั้งแต่ 1000 nm ถึง 1350 nm เก็บสะสมผลความเข้มโหมดแสง TM0 ทุกครั้งและรวบรวมทำกราฟ พบว่าความเข้มโหมดแสง TM0 เปลี่ยนแปลงเมื่อค่าดัชนีหักเหแสงของชั้นสารบนแผ่นฟิล์มทองเปลี่ยนแปลง และเกิดการเลื่อนเหลื่อมกันของพีคความเข้มโหมแสง TM0 ต่ำสุดที่ความยาวคลื่นต่างๆ กัน ของแต่ละค่าดัชนีหักเหแสงและเกิดขึ้นหลายตำแหน่งในช่วงความยาวคลื่นที่ป้อนเข้าแสดงถึงนัยสำคัญที่ดีเยี่ยมในการประยุกต์เป็นอุปกรณ์ตรวจรับรู้การเปลี่ยนแปลงภายนอกท่อนำแสง
##plugins.generic.usageStats.downloads##
##plugins.themes.bootstrap3.article.details##
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Chen, Y., & Ming, H. (2012). Review of surface plasmon resonance and localized surface plasmon resonance sensor. Photonic Sensors, 2(1), 37-49.
Du, C. H., & Chiou, Y. P. (2014). Vertical directional couplers with ultra-short coupling length based on hybrid plasmonic waveguides. Journal of lightwave technology, 32(11), 2065-2071.
Delacour, C., Blaize, S., Grosse, P., Fedeli, J. M., Bruyant, A., Salas-Montiel, R., Chelnokov, A. (2010). Efficient directional coupling between silicon and copper plasmonic nanoslot waveguides: toward metal-oxide-silicon nanophotonics. Nano letters, 10(8), 2922-2926.
Dellagiacoma, C., Lasser, T., Martin, O. J. F., Degiron, A., Mock, J. J., & Smith, D. R. (2011). Simulation of complex plasmonic circuits including bends. Optics Express, 19(20), 18979-18988.
Fu, Y., Hu, X., Lu, C., Yue, S., Yang, H., & Gong, Q. (2012). All-optical logic gates based on nanoscale plasmonic slot waveguides. Nano letters, 12(11), 5784-5790.
Han, Z., Elezzabi, A. Y., & Van, V. (2010). Wideband Y-splitter and aperture-assisted coupler based on subdiffraction confined plasmonic slot waveguides. Applied Physics Letters, 96(13), 131106.
LATIFI, H., ZIBAII, M. I., HOSSEINI, S. M., & JORGE, P. (2012), Nonadiabatic Tapered Optical Fiber for Biosensor Applications. Photonic Sensors, 2(4), 340–356.
Li, C. S., & Sun, H. (2012). Metamaterials Application in Sensing. Sensors, 12(3), 2742-2765.
Nemova, G., & Kashyap, R. (2007). Novel fiber Bragg grating assisted plasmon-polariton for bio-medical refractive-index sensors. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 18(1), 327-330.
Osowiecki, G. D., Barakat, E., Naqavi, A., & Herzig H. P. (2014). Vertically Coupled Plasmonic Slot Waveguide Cavity for Localized Bio-sensing applications. Optics Express, 22(17), 20871-20880.
Roney, T., Ikonic, Z., & Kelsall, R. W. (2012). Silicon based plasmonic coupler. Optics Express, 20 (19), 21520-21531.
Tan, Y. (2018). Chemical Sensing Applications of Carbon Nanotube-Deposited Optical Fibre Sensors. Chemo sensors, 6 (4), 55.
Wang, J., Cheng, Z., Chen, Z., Wan, X., Zhu, B., Tsang, H. K., ... Xu, J. (2016). High-responsivity graphene-on-silicon slot waveguide photodetectors. Nanoscale, 8(27), 13206-13211.
Zhu, Z., Garcia-Ortiz, C. E., Han, S., Radko, I. P., & Bozhevolnyi, S. I. (2013). Compact and Broadband Directional Coupling and Demultiplexing in Dieletric-loaded Surface Plasmon Polariton Waveguides Based on the Multimode Interference Effect. Applied Physics Letters, 103(6), 061108.