Serodiagnosis of map infection by latex agglutination test in slaugtered buffaloes of Malwa region (M.P., India)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56825/bufbu.2022.4143817Keywords:
Bubalus bubalis, buffaloes, anti-MAP antibodies, Crohn’s disease, Dot-ELISA, Johne’s diseaseAbstract
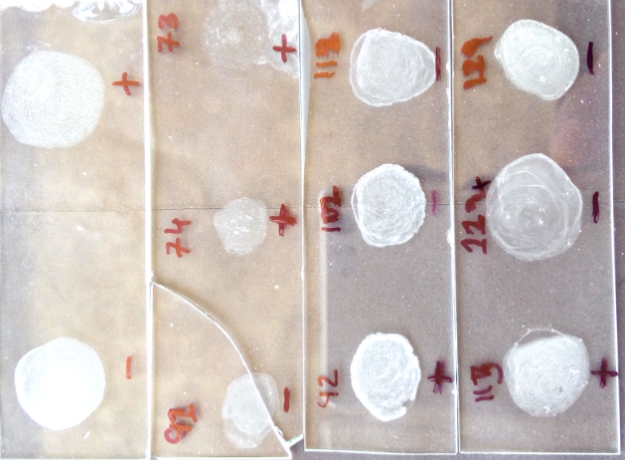
Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis (MAP) is the causative agent of chronic enteritis which is commonly called as Johne’s disease (JD) in animals which is associated with several incurable, auto-immune diseases like Crohn’s disease in human beings. In the current study, 19 serum samples of buffaloes were collected irrespective of their age, sex and breed which were slaughtered at Cantonment board slaughterhouse, Mhow and Nagar Nigam, Indore. These animals were brought from different places of Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh. For detection of anti-MAP antibodies, the latex agglutination test was performed following the standard procedure (Cheong Koo et al., 2004). The present investigation recorded 52.63% MAP infection in slaughtered buffaloes.
Downloads
Metrics
References
Singh, S.V., B.J. Stephen, M. Singh, S. Gupta, K. Chaubey, Sahzad, T.K. Sachan, J.S. Sohal, K. Dhama, S. Mukartal and Z. Hemati. 2016. Comparison of newly standardized ‘Latex milk agglutination test’, with ‘Indigenous milk ELISA’ for ‘on spot’ screening of domestic livestock against Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection. Indian J. Biotechnol., 15(4): 511-517.
Stephen, B.J., M. Singh, S.V. Singh, S. Gupta, K. Choubey, Sahzad, S. Jayaraman, M. Jain, J.S. Sohal, S. Mukartal and K. Dhama. 2016. Bio-contamination estimates of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis in fresh cottage cheese (Paneer) sold in rural, semi-urban and peri-urban regions of South Uttar Pradesh using multiple diagnostic tests. Advances in Animals and Veterinary Sciences, 4(8): 441-449. DOI: 10.14737/journal.aavs/2016/4.8.441.448








.png)








